Key Steps for SAP BO to Tableau Migration
Transitioning from WebI to Tableau for BI
USEReady’s Guide to WebI Reports Migration
Introduction to WebI and Tableau Migration
Challenges in Migrating SAP BO Reports
Best Practices for a Successful Migration
Tools and Techniques for Migrating to Tableau
Overview of SAP BO WebI and Tableau
Steps for Preparing Your Data for Migration
Automating the Migration Process
Case Studies of Successful Migrations
SAP BO WebI is a reporting and analytics tool that allows users to create, manage, and interact with reports from various sources. Accessible via a web-based interface, it helps to visualize data through charts and tables and perform ad-hoc analysis. It lets users drill down data and derive actionable insights.
Migrating SAP BO Web Intelligence (Webi) reports can be challenging, but it is essential to transition to advanced visualization or data analytics platforms to enhance capabilities and leverage modern features.
In this blog we will explore the process of migrating SAP BO WebI reports to Tableau. We’ll delve into the strategic benefits of this transition, the key steps involved in the migration process, and best practices to ensure a smooth transformation of your BI ecosystem.
Advantages of Moving WebI Reports to Tableau
First up, the benefits of upgrading WebI reports to Tableau… from legacy to modern BI.
- User Experience: Modern platforms like Tableau offer intuitive interfaces and interactive features, making it easier for users to create, customize, and navigate reports.
- Advanced Analytical and Visualization Capabilities: Tableau provides sophisticated analytical features and a wide array of visualization options, enabling deeper data exploration, more insightful interpretations, and more effective data presentation for informed decision-making.
- Improved Performance: Tableau can handle large volumes of data more efficiently, resulting in faster query performance and more responsive reports.
- Enhanced Integration Options: Advanced tools like Tableau typically offer improved integration capabilities, allowing seamless connectivity with diverse data sources and systems.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Modern BI platforms like Tableau are more scalable and adaptable, accommodating growing data needs and evolving business requirements with greater ease.
Migration Framework
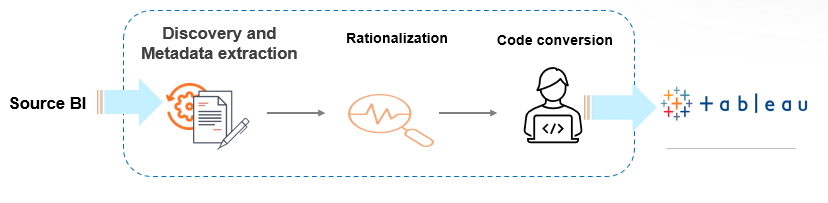
Key Steps in the Migration Process
Step 1
Discovery and Metadata Extraction
WebI report environment discovery involves analyzing and understanding the configuration, assessing report dependencies, performance, and optimization needs within the BI environment. Extracting report metadata involves retrieving detailed information about a report’s components such as:
- Data Sources: Details about the sources from which the report retrieves data, including connections to databases, universes, or other data repositories.
- Query Configurations: Metadata associated with the queries used to extract data, encompassing filters, prompts, and calculations.
- Report Layout: Information about the organization and design of the report, including its sections, blocks, and formatting guidelines.
- Variables and Calculations: Definitions of custom variables and formulas utilized within the report to manipulate or generate data.
- Data Objects and Attributes: Descriptions of the elements, such as dimensions, measures, and attributes, that are employed in the report to present data.
- Interactive Elements: Metadata on features like dynamic prompts and predefined filters that allow users to tailor their data views.
- Access Controls and Roles: Details about user roles and permissions that determine who can view, edit, or manage the reports.
Step 2
Rationalization
Rationalization utilizes extracted metadata to facilitate the migration of necessary documents to new analytics systems. Key activities involved include:
- Exclude Unused Reports: Remove reports that are no longer relevant or in use.
- Identify and Eliminate Duplicate Reports: Detect and consolidate duplicate reports to avoid redundancy.
- Consolidate Related Reports: Streamline and merge reports that cover similar data to enhance clarity and efficiency.
- Revise KPIs to Deliver More Meaningful Insights: Update Key Performance Indicators to ensure they provide actionable and relevant insights.
- Assess Data Quality: Evaluate and clean the data to ensure accuracy and reliability in the new system.
Step 3
Code Conversion
Transitioning from a legacy reporting tool to a more advanced system typically requires several essential code conversion steps.
Below is a high-level overview:
- Syntax Alignment: Modify queries to align with the syntax and functionalities of the new reporting tool. This may involve updating SQL dialects, functions, and operators to match the new system’s requirements.
- Report Layout Changes: Redesign or update existing BI report layouts and visualizations to match the new analytics tool interface and design options. This might involve re-creating charts, tables, and dashboards.
- Feature Mapping: List and map legacy functionalities (e.g., custom calculations, aggregations) to their equivalents in the advanced visualization tool. Some features may need to be re-implemented or replaced with alternative solutions.
- Connection Updates: Update database connections and integration points to ensure compatibility with the new analytics tool. This may include updating connection strings, authentication methods, and data sources.
- Performance Enhancement: Review and optimize queries and processes to leverage the new analytics tool’s performance features.
- Testing and Validation: Perform thorough testing on converted reports and processes to ensure accuracy, functionality, and performance. Compare with the legacy BI system to validate the migration.
These steps facilitate a seamless transition while preserving the integrity and effectiveness of your reporting capabilities.
Conclusion
Migrating from SAP BO WebI to Tableau is significant step up for users in modernizing their organization’s BI. It not only has the potential to enhance their analytics but also empower them with more intuitive and powerful reporting tools. The key to migration success however, lies in careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and a clear vision.











 Media Coverage
Media Coverage Press Release
Press Release
