Advancing Retail: Harnessing the Power of Advanced Analytics
Case Studies in Retail Innovation: Real-World Examples of Data-Driven Success
Evolving Retail Strategies: The Next Frontier of Data Analytics
How Will Analytics Help Retailers?
Some of the ways in which Big Data could be of help to retail businesses are:
- Identifying and creation of Client Profiles: Today retailers have a better way to identify the customers and offer them the right product. The customer segmentation is now much more refined, and data driven based on customers transaction history, basket analysis, loyalty programs, social media interactions. Big Data management segment buyer’s data to create personality points, demarcating faceless mass into slots, through studying their purchases. Transaction reports and loyalty plans are combed through, to bring out relevant data and action on it. It is easier for retailers to get a 360-degree view of the customer and offer them customized products based on their past preferences or what people similar to them are buying.
- Price Optimization: Online retailing is based on dynamic pricing and the price of a product depends on multiple factors from market demand, inventory, competitors pricing, whether a particular product is the seasons must have product, etc. Data Analytics plays a vital role in determining the pricing. Algorithms track demand, inventory levels, and competitor activity and automatically respond to market changes in real time, allowing action to be taken based on insights in a time saving manner. It helps in determining when prices should be dropped – commonly known as ‘mark down optimization’. Prior to the age of analytics most retailers would just reduce prices at the end of a buying season for a particular product line when demand has almost gone. But now based on Machine Learning, prices are adjusted real time and recommendations or offers are sent to a specific set of customers who has purchased those products or has earlier shown interest to buy those.
- Generating Customer Loyalty: Customers today need to be treated royally, they want retailers to understand their requirement, recommend product and services that suits them, and keep them informed at every stage of the selling cycle from booking, shipping, and product delivery to feedback. This is not an easy task for the retailers keeping in mind the varied customers they serve. Big Data Analysis can help them to recommend the right products to a customer or come up with targeted marketing campaigns to reach out to a specific segment. It also helps you to understand the customers’ path to purchase or their buying pattern, thus reaching out to them at each step to close the sales cycle.
- Predicting Demand: Today retailers have advanced tools available to them in order to know the trends in the industry. Forecasting demand has become much more efficient now and retailers can easily find if a particular product is in demand during certain time of the year, or in a particular city or by a specific group and how to adjust the inventory. Retailers also gather a lot of data from social media to understand the changing preferences of customers or do sentiment analysis to find whether the product is getting positive, negative, or neutral feedback in the market.
- Inventory Management: Trend forecasting algorithms sort through the buying data to analyze what marketing departments need to promote and what not. Once the retailers get a deep insight into buying trends of the customers, they focus on the sectors where there will be high demand. This involves gathering demographic, seasonal, occasions led data and economic indicators to build a picture of purchase behaviour across the targeted market. This really helps in inventory management in a better way.
- Identify the highest ROI Opportunities: Each customer interaction can have a large impact on existing or potential relationships. Rolling out a new idea to the whole sales force is a risky endeavour, as a wrong decision could lead to immediate as well as prolonged loss of profit. Instead, leading business organizations have found that the best way to isolate the cause-and-effect relationship between any strategic shift and key performance indicators through use of a test-and-learn approach – trying an idea with some sets of customers and comparing the performance of the ‘test’ group to the performance of a well-matched ‘control’ group. After having a better understanding of their current and potential customer base, retailers use predictive risk filters and data-driven intelligence to model expected responses in marketing campaigns, as measured by propensity to buy / likely to buy.
- Fraud Detection: Big Data Analytics can be effectively used to detect any fraud by analyzing data from daily transactions and activities such as purchasing, accounts payable, sales projections, warehouse movements, employee shift records, returns and store-level video and audio recordings.
The Retail Analytics Framework
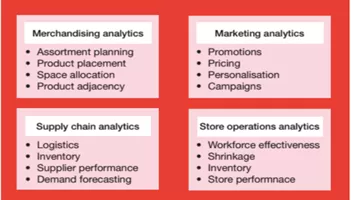
- Merchandising Analytics: Retailers can use merchandising analytics to stock the right product at the right place at the right time. Merchandising analytics enable planners to align their merchandising decisions with customer expectations. The key areas of merchandising analytics are assortment planning, product adjacency and space allocation. Analytics holds the key to optimizing assortment. For each stock keeping unit (SKU), retailers can identify a few attributes, such as brand, package size or flavor, that are meaningful to customers. They can then use the sales of existing SKUs to estimate the future demand at attribute level and further use these estimates to forecast the demand for any combination of attributes, including those that correspond to new products the retailer is considering adding to its assortment.
- Marketing Analytics: To keep up with changing customer demands and ensure loyalty, retailers need marketing analytics for deeper customer insight, targeted interactions, and improved customer service. Marketing analytics quickly combine all relevant customer data – from point of sale (POS) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) system, loyalty cards, etc., with social media data – perform sophisticated analytics, and share insights to help optimize marketing decisions. It can also help to optimize multichannel performance, improve marketing effectiveness, and enhance social media presence.
- Supply Chain Analytics: Retail profitability is directly impacted by the logistics efficiency to maximize demand fulfilment and avoid any back orders or stock-outs. These include interventions in logistics, inventory, and supplier performance. Advanced analytics solutions using a global positioning system (GPS) can help in tracking the movement of the fleet, understanding the behaviours of the drivers, identifying hazard points on the routes, etc. This can help in reducing the overall costs, make logistics safer and efficient.
- Store Operation Analytics: More and more retailers are adding sensors to people, places, processes, and products in order to gather and analyze information for better decision-making and greater transparency. Predictive analytics applications process this data, optimize the supply chain, and decrease inventory shrink. Retail stores are increasingly adopting sensors to determine inventory levels and restock shelves automatically. Location analytics can map how customers move through a store. Using a combination of IoT (Internet of Things) – enabled product and shelf sensors, cameras, and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) devices, one can track which sections of the store receive the most traffic in general over different hours of the day and week. Going forward, retailers can view IoT as a tool that enables them to help their customers through innovations such as smart price tags that can change prices in real time, mirrors that allow a person to try clothes on virtually, and packaging that monitors the freshness of goods and alerts the consumer when they are nearing the end of their shelf life.
Challenges in Retail Analytics
Advanced Analytics: Driving Innovation in Retail
Real-World Success: Case Studies of Retailers Embracing Data Analytics
Future Directions: Innovations and Trends Shaping Retail Analytics
Implementing Advanced Analytics: Strategies for Retailers
Going Beyond Basics: Exploring Advanced Analytics in Retail
Success Stories: How Retailers Are Leveraging Advanced Analytics for Growth
The Next Wave: Emerging Technologies and Techniques in Retail Analytics
Strategies for Success: Implementing Advanced Analytics in Retail Operations
Retailers have already started putting data analytics at the heart of their operations across the value chain – procurement, supply chain, sales and marketing, store operations, and customer management. However, they now need to establish a big data ecosystem, which processes multiple terabytes of new data and petabytes of historical data, which will help them improve their revenues via analytics-based decision-making. While this may sound really exciting, big data management and analysis comes with its own set of challenges.
Several issues will have to be kept in mind to optimize the full capabilities of big data. Privacy, security, intellectual property, and even liability policies need to be stringent in terms of big data. Since big data encapsulates high end analytics, specially trained professionals need to be added to the team to utilize and functionalize the big data.
Companies need to integrate information from multiple data sources, often from third parties, as well as deploy an efficient data to aid such an environment. Many times, companies fall in shortsightedness, failing to implement insights from analytics. However, this could be fixed by continuous alterations of retail styles where a certain team is allotted for task of arrangement of insights and their implementation.


