Secure Authentication for Embedded Tableau Content: A Golang Approach
Enhancing Security: Golang-Based Authentication for Tableau Integration
Implementing Secure Authentication with Golang for Embedded Tableau Content
Tableau-connected apps enable a seamless and secure authentication experience by facilitating an explicit trust relationship between your Tableau Online/Server Site and custom applications where Tableau content is embedded. The trust relationship between your Tableau Online site and custom application is established and verified through an authentication token in the JSON Web Token (JWT) standard, which uses a shared secret provided by the Tableau-connected app and signed by your custom application.
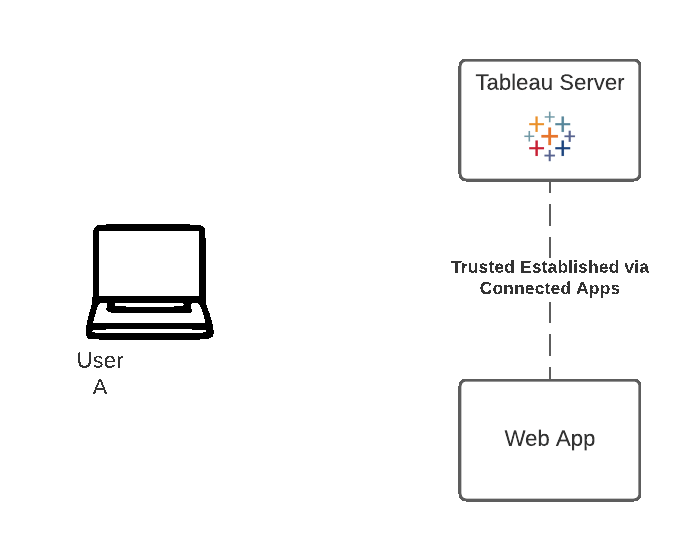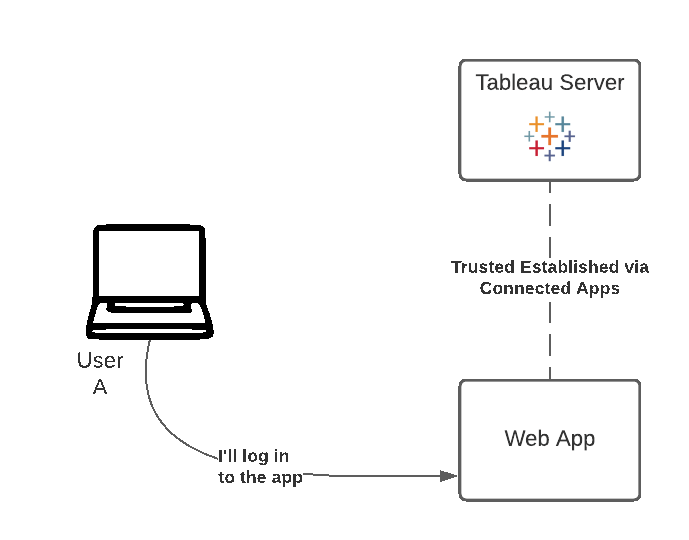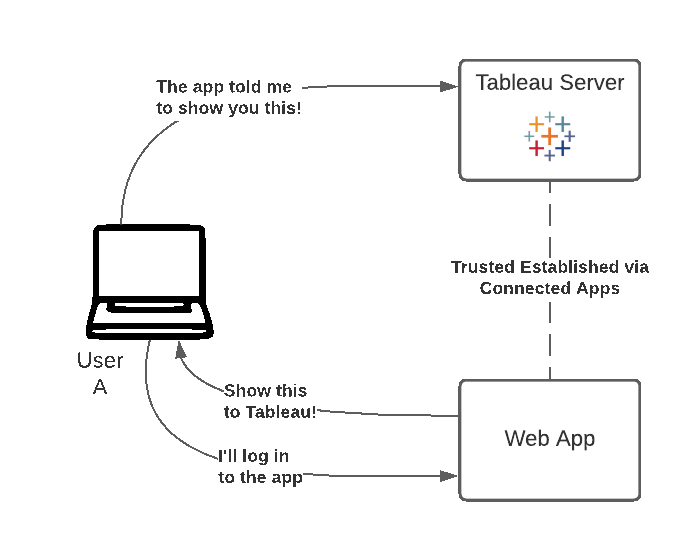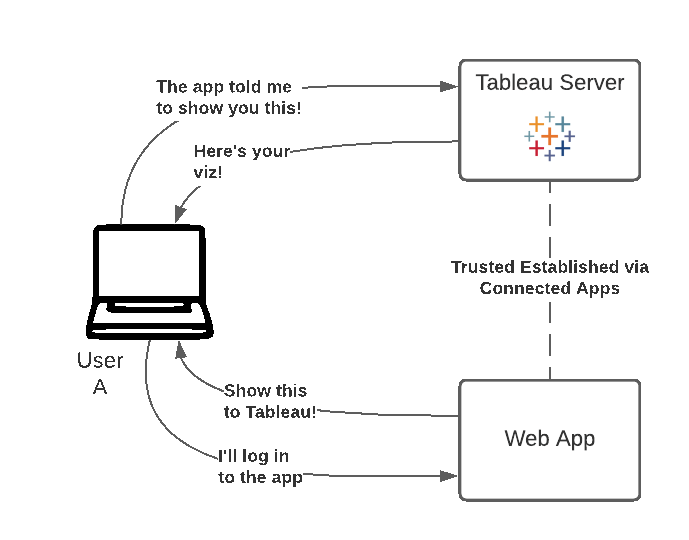
There are two types of connected apps you can configure:
1. Using direct trust, you can:
- Restrict access to which content can be embedded and where that content can be embedded
- Provide users the ability to access embedded content using single sign-on (SSO) without having to integrate with an identity provider (IdP)
- Provide users the ability to authenticate directly from your custom application
- Programmatically authorize access to Tableau REST API on users’ behalf using JSON Web Token (JWT)
- Scope Tableau REST API capabilities users or applications can perform
For more information about this connected app type, see Configure Connected Apps with Direct Trust.
2. Using OAuth 2.0 trust, you can: (Coming soon)
- Restrict access to which content can be embedded and where that content can be embedded
- Provide users the ability to access embedded content using single sign-on (SSO) through your identity provider (IdP)
- Provide access using standard OAuth 2.0 standard protocol
- Programmatically authorize access to Tableau REST API on users’ behalf
- Scope Tableau REST API capabilities users or applications can perform
For reference, please check here for the steps to configure connected apps with direct trust.
Background and Requirements
You’ll need:
- TOL or Tableau server > 2021.4
- Site Admin rights on Tableau Online, Server Administrator on Tableau Server
- Javascript skills, other languages examples available on our official documentation: https://help.tableau.com/current/online/en-us/connected_apps.htm
We strongly encourage you to use a sandbox environment, you can get one for free with our Developer Program:
- Join the Developer Program: https://www.tableau.com/developer
- Request your free dev site: https://www.tableau.com/developer/get-site
Understanding Golang-Based Authentication for Tableau Integration
Benefits of Using Golang for Secure Authentication
Best Practices for Securely Embedding Tableau Content in Custom Apps
Golang Implementation: Steps for Secure Authentication with Tableau
Introduction to Secure Authentication for Embedded Tableau Content
Why Choose Golang for Authentication in Tableau Integration?
Secure Authentication Implementation: Golang and Tableau Integration
Ensuring Data Security: Key Considerations for Embedded Tableau Content
Key Benefits:
- Restrict access to which content can be embedded and where that content can be embedded
- Provide users the ability to access embedded content using single sign-on (SSO) without having to integrate with an identity provider (IdP)
- Single point of control (delete, rotate secrets…) for a better governance
- Provide users the ability to authenticate directly from your custom application
- Secure by design using JWT open standard defining a self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed using a secret with the HMACalgorithm
What makes this blog different from others?
Today, Tableau provides JWT code samples in both Java and Python, but there is no quick example in Golang for creating a JWT. The reason is that there are many web applications built with Golang and they do not want to change the coding language. There is no need to worry anymore!
You are at the right place to get the sample code and deployment instructions that help to create a JWT using Golang.
Here you go with the sample Golang code, Payload
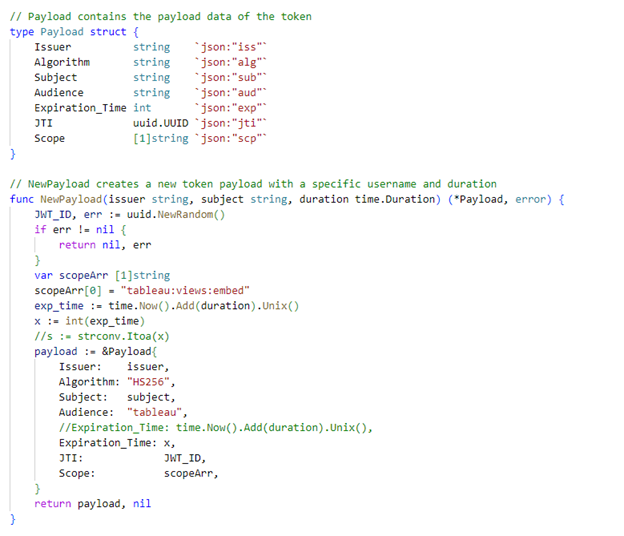
Token Creation
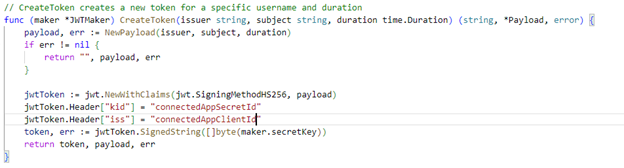
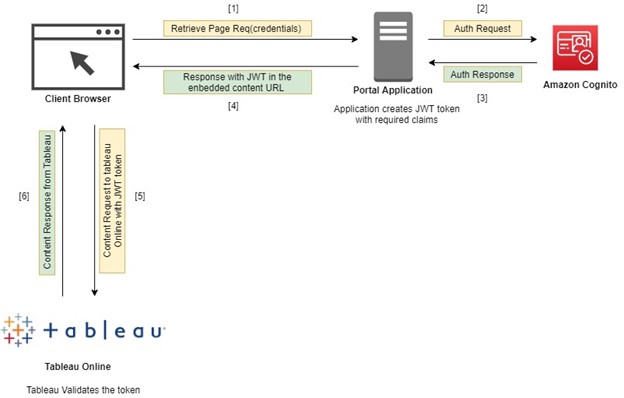
How we solved the problem?
Workflow Diagram
Conclusion:
Authentication can be seen as an important technical security piece but it’s also strongly influenced the user experience. When comes the time to decide the way you going to handle authentication, security and flexibility are important.
Connected Apps will give you both and will ensure the best user experience with Single Sign-On (SSO). Think about Connected Apps as an authentication abstraction in between your application and Tableau. You don’t need to know by which method your users are authenticated in your application. The only information you’ll need to create a Tableau session is the user id.
It is easy to set up and IDP integrations with Tableau is no longer required, no need to setup SAML/OpenID etc. In some situations, it is even impossible to rely on IDP integration.
Connected Apps streamlines the authentication experience with a unique way to create user sessions (with restricted scopes if you need to narrow the default authorizations) for Tableau Online (TOL) and Tableau Server (on-prem). This is especially important for TOL and embedded projects, knowing Trusted Authentication is not supported.
Your final takeaway would be that you are now ready to use GoLang to transmit information securely between two parties.











 Media Coverage
Media Coverage Press Release
Press Release

